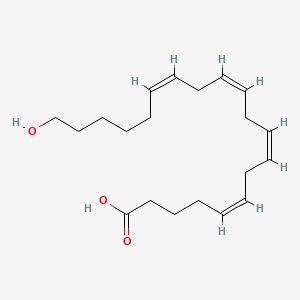
20-HETE
20-hete is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 20-hete is associated with abnormalities such as Cyst, Kidney Diseases, Kidney Failure, Chronic, Cystic Kidney Diseases and Simple renal cyst. The involved functions are known as Phosphorylation, inhibitors, Hypertrophy, Epithelial Cell Proliferation and Anabolism. 20-hete often locates in Mouse Kidney, Microsomes, Tissue membrane, Body tissue and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with 20-HETE are CYP4F3 gene, PKHD1 gene, Transgenes, P4HTM gene and CYP2E1 gene. The related lipids are Promega, enterodiol, Fatty Acids, hexanoic acid and U 73343. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Knock-out, Streptozotocin Diabetes, Transgenic Model and Rodent Model.
References related to pathways published in Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10899074 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2000 | Sun CW et al. | Role of cGMP versus 20-HETE in the vasodilator response to nitric oxide in rat cerebral arteries. |
| 11179048 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2001 | Frisbee JC et al. | 20-HETE modulates myogenic response of skeletal muscle resistance arteries from hypertensive Dahl-SS rats. |
| 11668070 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2001 | Zhao X et al. | The CYP450 hydroxylase pathway contributes to P2X receptor-mediated afferent arteriolar vasoconstriction. |
| 12521947 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2003 | Amaral SL et al. | CYP4A metabolites of arachidonic acid and VEGF are mediators of skeletal muscle angiogenesis. |
| 15964920 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2005 | Takeuchi K et al. | Reversal of delayed vasospasm by an inhibitor of the synthesis of 20-HETE. |
| 16782846 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2006 | Fang X et al. | 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid is a potent dilator of mouse basilar artery: role of cyclooxygenase. |
| 17114243 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2007 | Marvar PJ et al. | High dietary salt reduces the contribution of 20-HETE to arteriolar oxygen responsiveness in skeletal muscle. |
| 18156192 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2008 | Cheng J et al. | 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid causes endothelial dysfunction via eNOS uncoupling. |
| 18203846 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2008 | Morin C et al. | Effects of omega-hydroxylase product on distal human pulmonary arteries. |
| 18952718 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2008 | Dunn KM et al. | Elevated production of 20-HETE in the cerebral vasculature contributes to severity of ischemic stroke and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats. |
| 19136601 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2009 | Dhanasekaran A et al. | 20-HETE increases survival and decreases apoptosis in pulmonary arteries and pulmonary artery endothelial cells. |
| 19502554 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2009 | Guo AM et al. | 20-HETE can act as a nonhypoxic regulator of HIF-1alpha in human microvascular endothelial cells. |
| 20675568 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2010 | Zeng Q et al. | 20-HETE increases NADPH oxidase-derived ROS production and stimulates the L-type Ca2+ channel via a PKC-dependent mechanism in cardiomyocytes. |
| 21239640 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2011 | Tsai IJ et al. | 20-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid synthesis is increased in human neutrophils and platelets by angiotensin II and endothelin-1. |
| 21257913 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2011 | Harder DR et al. | Pressure-induced myogenic tone and role of 20-HETE in mediating autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. |
| 24097425 | Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. | 2013 | Toth P et al. | Role of 20-HETE, TRPC channels, and BKCa in dysregulation of pressure-induced Ca2+ signaling and myogenic constriction of cerebral arteries in aged hypertensive mice. |