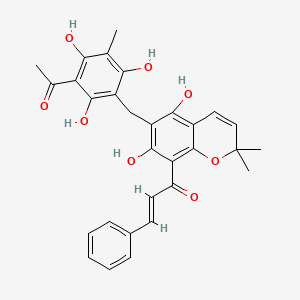
rottlerin
Rottlerin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Rottlerin is associated with abnormalities such as PARAGANGLIOMAS 2, Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal, Virus Diseases, Perisylvian syndrome and Autoimmune disease (systemic) NOS. The involved functions are known as Apoptosis, Regulation, Signal Transduction, inhibitors and Proteasome Inhibitors [MoA]. Rottlerin often locates in Clone, Membrane, Body tissue, Plasma membrane and soluble. The associated genes with Rottlerin are XIAP gene, GAPDH gene, ICAM1 gene, P4HTM gene and TNFSF10 gene. The related lipids are Promega, Fatty Acids, Sphingolipids, Lipopolysaccharides and Saponin. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Xenograft Model and Cancer Model.
References related to abnormalities published in Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11133494 | Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. | 2001 | De Witt BJ et al. | Effects of PKC isozyme inhibitors on constrictor responses in the feline pulmonary vascular bed. |
| 15489375 | Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. | 2005 | Woo CH et al. | VCAM-1 upregulation via PKCdelta-p38 kinase-linked cascade mediates the TNF-alpha-induced leukocyte adhesion and emigration in the lung airway epithelium. |
| 16040631 | Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. | 2005 | Brown JM et al. | Effects of rottlerin on silica-exacerbated systemic autoimmune disease in New Zealand mixed mice. |