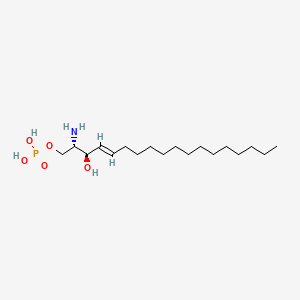
Sphingosine 1-phosphate
Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Sphingosine 1-phosphate is associated with abnormalities such as Infection, Painful Bladder Syndrome, Atherosclerosis, Hyperglycemia and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The involved functions are known as Phosphorylation, Regulation, enzyme activity, Energy Absorption and Vascular Permeability. Sphingosine 1-phosphate often locates in Endothelium, Tissue membrane, Vascular System, Protoplasm and Microfilaments. The associated genes with Sphingosine 1-phosphate are MBTPS1 gene, FBXL15 gene, TEK gene, NTRK1 gene and Gene Family. The related lipids are Promega, Lipopolysaccharides, lysophosphatidic acid, Lysophosphatidylcholines and Lysophospholipids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Transgenic Model, Disease model and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis.
References related to experimental models published in Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20702813 | Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | 2010 | Medlin MD et al. | Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 signals through leukemia-associated RhoGEF (LARG), to promote smooth muscle cell differentiation. |
| 19164813 | Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | 2009 | Gaengel K et al. | Endothelial-mural cell signaling in vascular development and angiogenesis. |
| 20431071 | Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | 2010 | Yoshida T et al. | Therapeutic angiogenesis by implantation of a capillary structure constituted of human adipose tissue microvascular endothelial cells. |
| 17569880 | Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. | 2007 | Kontush A et al. | Preferential sphingosine-1-phosphate enrichment and sphingomyelin depletion are key features of small dense HDL3 particles: relevance to antiapoptotic and antioxidative activities. |