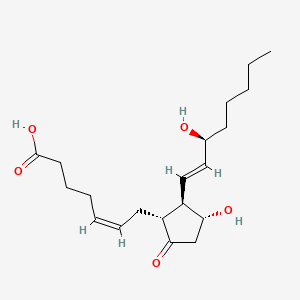
Prostaglandin E2
Prostaglandin E2 is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Prostaglandin e2 is associated with abnormalities such as Renal glomerular disease, Arthritis, Degenerative polyarthritis, Pancreatitis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. The involved functions are known as enzyme pathway, Atherogenesis, Anabolism, inhibitors and Oxidants. Prostaglandin e2 often locates in Tissue membrane, Blood, Extracellular, Membrane and Protoplasm. The associated genes with Prostaglandin E2 are PTGS2 gene, TP53 gene, TNFRSF5 gene, FASTK Gene and TNF gene. The related lipids are Lipopolysaccharides, Steroids, monooxyethylene trimethylolpropane tristearate, Fatty Acids, Unsaturated and Promega. The related experimental models are Arthritis, Adjuvant-Induced, Xenograft Model, Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis, Cancer Model and Knock-out.
References related to experimental models published in Biochem. Pharmacol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26123522 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | 2015 | Koeberle A and Werz O | Perspective of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 as drug target in inflammation-related disorders. |
| 24355567 | Biochem. Pharmacol. | 2014 | Schiffmann S et al. | PGE2/EP4 signaling in peripheral immune cells promotes development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. |