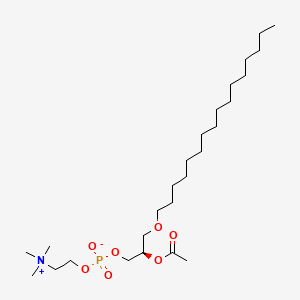
Platelet activating factor
Platelet activating factor is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. Platelet activating factor is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Acute cholecystitis without calculus, Cholecystitis, Colitis and Cholecystitis, Acute. The involved functions are known as Cell Survival, Metabolic Inhibition, lipid oxidation, Apoptosis and Oxidation. Platelet activating factor often locates in soluble, Cellular Membrane, Smooth muscle (tissue), Intima and Tissue specimen. The associated genes with Platelet activating factor are apolipoprotein A-I Milano, Homologous Gene, TSPO gene, HBEGF gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are Hydroxycholesterols, Liposomes, 25-hydroxycholesterol, Lysophosphatidylcholines and Lipopolysaccharides. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model and Transgenic Model.
References related to genes published in Blood
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2451547 | Blood | 1988 | Vercellotti GM et al. | Platelet-activating factor primes neutrophil responses to agonists: role in promoting neutrophil-mediated endothelial damage. |
| 8608226 | Blood | 1996 | Gabbeta J et al. | Abnormal inside-out signal transduction-dependent activation of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa in a patient with impaired pleckstrin phosphorylation. |
| 22167755 | Blood | 2012 | López-Sagaseta J et al. | sPLA2-V inhibits EPCR anticoagulant and antiapoptotic properties by accommodating lysophosphatidylcholine or PAF in the hydrophobic groove. |