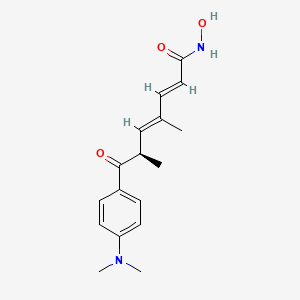
trichostatin A
Trichostatin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Trichostatin is associated with abnormalities such as Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy, PARAGANGLIOMAS 3, abnormal fragmented structure, Disintegration (morphologic abnormality) and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Acetylation, Cell Differentiation process, histone modification, Gene Silencing and Transcriptional Activation. Trichostatin often locates in CD41a, Hematopoietic System, Chromatin Structure, Blood and Endothelium. The associated genes with Trichostatin are SPI1 gene, CELL Gene, Chromatin, CXCR4 gene and DNMT1 gene. The related lipids are Butyrates, Promega, butyrate, Lipopolysaccharides and Steroids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model and Cancer Model.
References related to locations published in EMBO J.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9430643 | EMBO J. | 1998 | Wong J et al. | Distinct requirements for chromatin assembly in transcriptional repression by thyroid hormone receptor and histone deacetylase. |
| 11250901 | EMBO J. | 2001 | Muth V et al. | Acetylation of TAF(I)68, a subunit of TIF-IB/SL1, activates RNA polymerase I transcription. |
| 12743043 | EMBO J. | 2003 | Craig JM et al. | Centromeric chromatin pliability and memory at a human neocentromere. |
| 10329635 | EMBO J. | 1999 | O'Neill LP et al. | A developmental switch in H4 acetylation upstream of Xist plays a role in X chromosome inactivation. |
| 15660132 | EMBO J. | 2005 | Schmittwolf C et al. | In vivo haematopoietic activity is induced in neurosphere cells by chromatin-modifying agents. |