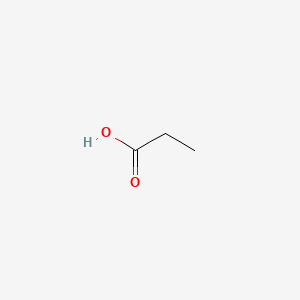
propionic acid
propionic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Propionic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Epilepsy, Infection, Tuberculosis, Alkalosis and Ischemia. The involved functions are known as Uptake, Biosynthetic Pathways, Methylation, Protein Overexpression and Biochemical Pathway. Propionic acid often locates in Body tissue, Cytoplasmic matrix, Membrane, Protoplasm and Extracellular. The associated genes with propionic acid are TRIO gene, TRRAP gene, SLC5A8 gene, SLC33A1 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Propionate, butyrate, Valerates and mycocerosic acid.
References related to genes published in J. Bacteriol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10940008 | J. Bacteriol. | 2000 | Takahashi N et al. | Metabolic pathways for cytotoxic end product formation from glutamate- and aspartate-containing peptides by Porphyromonas gingivalis. |
| 12730158 | J. Bacteriol. | 2003 | Sirakova TD et al. | Attenuation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by disruption of a mas-like gene or a chalcone synthase-like gene, which causes deficiency in dimycocerosyl phthiocerol synthesis. |
| 18281403 | J. Bacteriol. | 2008 | Doughty DM et al. | Evidence for involvement of copper ions and redox state in regulation of butane monooxygenase in Pseudomonas butanovora. |
| 16585772 | J. Bacteriol. | 2006 | Nakayama S and Watanabe H | Mechanism of hilA repression by 1,2-propanediol consists of two distinct pathways, one dependent on and the other independent of catabolic production of propionate, in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. |
| 18456814 | J. Bacteriol. | 2008 | Bainbridge BW et al. | Acyl chain specificity of the acyltransferases LpxA and LpxD and substrate availability contribute to lipid A fatty acid heterogeneity in Porphyromonas gingivalis. |