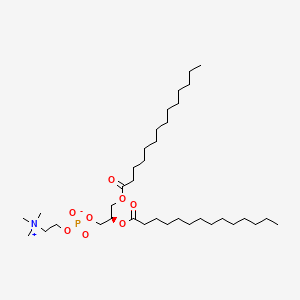
18194-24-6
18194-24-6 is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. 18194-24-6 is associated with abnormalities such as Cerebrovascular accident, Renal tubular disorder, Atherosclerosis, Hyperlipoproteinemia Type III and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. The involved functions are known as Process, protein folding, Catalyst, Biochemical Pathway and Fold in Medical Device Material. 18194-24-6 often locates in Tissue membrane, Membrane, periplasm, vesicle membrane and outer membrane. The associated genes with 18194-24-6 are Integral Membrane Proteins, Protein Structure, RTN4 gene, RTN4R gene and Protein, Organized by Structure. The related lipids are Micelles, dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol, 1,2-dihexadecyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, Unilamellar Vesicles and cholesteryl oleate. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Arthritis, Adjuvant-Induced, Disease model and Xenograft Model.
References related to abnormalities published in J. Biol. Chem.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8995232 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1997 | Riddell DR et al. | Apolipoprotein E inhibits platelet aggregation through the L-arginine:nitric oxide pathway. Implications for vascular disease. |
| 7829491 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1995 | Mishra VK et al. | Effect of the arrangement of tandem repeating units of class A amphipathic alpha-helixes on lipid interaction. |
| 11912196 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2002 | Ji ZS et al. | Apolipoprotein E4 potentiates amyloid beta peptide-induced lysosomal leakage and apoptosis in neuronal cells. |
| 12393895 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2002 | Morrow JA et al. | Apolipoprotein E4 forms a molten globule. A potential basis for its association with disease. |
| 12684504 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2003 | Kiss RS et al. | Structure-guided protein engineering modulates helix bundle exchangeable apolipoprotein properties. |
| 10567370 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1999 | Shen YM et al. | Lipid-dependent activation of protein kinase C-alpha by normal alcohols. |
| 10801877 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2000 | Lu B et al. | Conformational reorganization of the four-helix bundle of human apolipoprotein E in binding to phospholipid. |
| 10751422 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2000 | Klezovitch O et al. | Structural determinants in the C-terminal domain of apolipoprotein E mediating binding to the protein core of human aortic biglycan. |
| 18845546 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2008 | Mishra VK et al. | Effect of leucine to phenylalanine substitution on the nonpolar face of a class A amphipathic helical peptide on its interaction with lipid: high resolution solution NMR studies of 4F-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine discoidal complex. |
| 16407255 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2006 | Mishra VK et al. | Association of a model class A (apolipoprotein) amphipathic alpha helical peptide with lipid: high resolution NMR studies of peptide.lipid discoidal complexes. |
| 15485851 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2004 | Bender V et al. | T cell antigen receptor peptide-lipid membrane interactions using surface plasmon resonance. |
| 15878877 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2005 | Lookene A et al. | Apolipoprotein A-V-heparin interactions: implications for plasma lipoprotein metabolism. |
| 16159879 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2005 | Pearson K et al. | Specific sequences in the N and C termini of apolipoprotein A-IV modulate its conformation and lipid association. |
| 23288849 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2013 | Deng X et al. | Small-angle X-ray scattering of apolipoprotein A-IV reveals the importance of its termini for structural stability. |
| 25398882 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2015 | Smrt ST et al. | The influenza hemagglutinin fusion domain is an amphipathic helical hairpin that functions by inducing membrane curvature. |