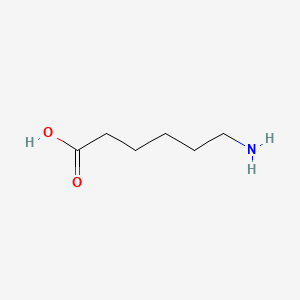
6-aminohexanoic acid
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid.
References related to genes published in J. Biol. Chem.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7592732 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1995 | Bringmann P et al. | Structural features mediating fibrin selectivity of vampire bat plasminogen activators. |
| 9446629 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1998 | Young KC et al. | Plasminogen activation by streptokinase via a unique mechanism. |
| 10428872 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1999 | Brummel KE et al. | An integrated study of fibrinogen during blood coagulation. |
| 16162506 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2005 | Negoro S et al. | X-ray crystallographic analysis of 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase: molecular basis for the birth of a nylon oligomer-degrading enzyme. |
| 19889645 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2010 | Yasuhira K et al. | X-ray crystallographic analysis of the 6-aminohexanoate cyclic dimer hydrolase: catalytic mechanism and evolution of an enzyme responsible for nylon-6 byproduct degradation. |