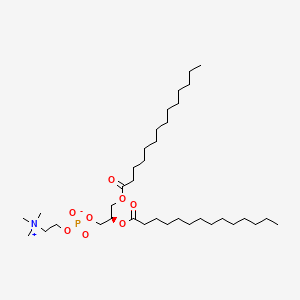
18194-24-6
18194-24-6 is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. 18194-24-6 is associated with abnormalities such as Cerebrovascular accident, Renal tubular disorder, Atherosclerosis, Hyperlipoproteinemia Type III and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. The involved functions are known as Process, protein folding, Catalyst, Biochemical Pathway and Fold in Medical Device Material. 18194-24-6 often locates in Tissue membrane, Membrane, periplasm, vesicle membrane and outer membrane. The associated genes with 18194-24-6 are Integral Membrane Proteins, Protein Structure, RTN4 gene, RTN4R gene and Protein, Organized by Structure. The related lipids are Micelles, dimyristoylphosphatidylglycerol, 1,2-dihexadecyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine, Unilamellar Vesicles and cholesteryl oleate. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Arthritis, Adjuvant-Induced, Disease model and Xenograft Model.
References related to genes published in J. Lipid Res.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9643348 | J. Lipid Res. | 1998 | Dong LM et al. | The carboxyl terminus in apolipoprotein E2 and the seven amino acid repeat in apolipoprotein E-Leiden: role in receptor-binding activity. |
| 10064737 | J. Lipid Res. | 1999 | Daum U et al. | Multiple dysfunctions of two apolipoprotein A-I variants, apoA-I(R160L)Oslo and apoA-I(P165R), that are associated with hypoalphalipoproteinemia in heterozygous carriers. |
| 11254752 | J. Lipid Res. | 2001 | DeLozier JA et al. | Vesicle-binding properties of wild-type and cysteine mutant forms of alpha(1) domain of apolipoprotein B. |
| 11369796 | J. Lipid Res. | 2001 | Lund-Katz S et al. | Effects of polymorphism on the microenvironment of the LDL receptor-binding region of human apoE. |
| 12364553 | J. Lipid Res. | 2002 | Segall ML et al. | Influence of apoE domain structure and polymorphism on the kinetics of phospholipid vesicle solubilization. |
| 11060345 | J. Lipid Res. | 2000 | Liu H et al. | Characterization of the lipid-binding properties and lipoprotein lipase inhibition of a novel apolipoprotein C-III variant Ala23Thr. |
| 11060347 | J. Lipid Res. | 2000 | Dong J et al. | Human apolipoprotein E7:lysine mutations in the carboxy-terminal domain are directly responsible for preferential binding to very low density lipoproteins. |
| 21504968 | J. Lipid Res. | 2011 | Kateifides AK et al. | Alteration of negatively charged residues in the 89 to 99 domain of apoA-I affects lipid homeostasis and maturation of HDL. |
| 18984910 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | James PF et al. | Aromatic residues in the C-terminal helix of human apoC-I mediate phospholipid interactions and particle morphology. |
| 19098283 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | Wang YT et al. | Dimyristoylphosphotidylcholine induces conformational changes in apoB that lowers lipoprotein(a). |
| 18403317 | J. Lipid Res. | 2008 | Blanchette CD et al. | Quantifying size distributions of nanolipoprotein particles with single-particle analysis and molecular dynamic simulations. |
| 15805548 | J. Lipid Res. | 2005 | Zhu X et al. | Cysteine mutants of human apolipoprotein A-I: a study of secondary structural and functional properties. |
| 16061953 | J. Lipid Res. | 2005 | Barrow DJ et al. | Mechanistic studies on percutaneous penetration enhancement by N-(4-halobenzoyl)-S,S-dimethyliminosulfuranes. |
| 15654121 | J. Lipid Res. | 2005 | Hajj Hassan H et al. | Structural modification of plasma HDL by phospholipids promotes efficient ABCA1-mediated cholesterol release. |
| 15654128 | J. Lipid Res. | 2005 | Tricerri MA et al. | Visualization and analysis of apolipoprotein A-I interaction with binary phospholipid bilayers. |
| 16513897 | J. Lipid Res. | 2006 | Postle AD et al. | Lipidomics of cellular and secreted phospholipids from differentiated human fetal type II alveolar epithelial cells. |
| 23349207 | J. Lipid Res. | 2013 | Gogonea V et al. | The low-resolution structure of nHDL reconstituted with DMPC with and without cholesterol reveals a mechanism for particle expansion. |
| 23110818 | J. Lipid Res. | 2013 | Georgiadou D et al. | Thermodynamic and structural destabilization of apoE3 by hereditary mutations associated with the development of lipoprotein glomerulopathy. |