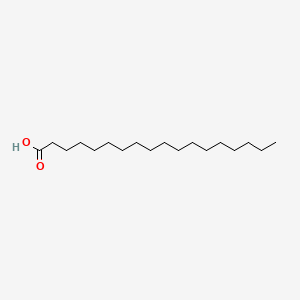
stearic acid
stearic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Stearic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Helminthiasis, Exanthema, Chronic disease, Obesity and Dyslipidemias. The involved functions are known as acyltransferase activity, Mutation, Cell division, cell fate and Fatty Acid Metabolism. Stearic acid often locates in membrane fraction, Mouse Liver, Membrane, Body tissue and Endoplasmic reticulum, membrane. The associated genes with stearic acid are Homologous Gene, ACLY gene, Transgenes, FATE1 gene and Alleles. The related lipids are Lysophospholipids, Stearic acid, Fatty Acids, cis-vaccenic acid and Phosphatidylserines. The related experimental models are Knock-out.
References related to lipids published in J. Lipid Res.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10508209 | J. Lipid Res. | 1999 | Summers LK et al. | Use of structured triacylglycerols containing predominantly stearic and oleic acids to probe early events in metabolic processing of dietary fat. |
| 10787438 | J. Lipid Res. | 2000 | Schmider W et al. | Transport of heptafluorostearate across model membranes. Membrane transport of long-chain fatty acid anions I. |
| 22172515 | J. Lipid Res. | 2012 | Imae R et al. | LYCAT, a homologue of C. elegans acl-8, acl-9, and acl-10, determines the fatty acid composition of phosphatidylinositol in mice. |
| 22628618 | J. Lipid Res. | 2012 | Masuda M et al. | Activating transcription factor 4 regulates stearate-induced vascular calcification. |
| 18387886 | J. Lipid Res. | 2008 | Lockridge JB et al. | Bioinformatic profiling of the transcriptional response of adult rat cardiomyocytes to distinct fatty acids. |
| 18812595 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | Kratzer A et al. | Synthetic LXR agonist attenuates plaque formation in apoE-/- mice without inducing liver steatosis and hypertriglyceridemia. |
| 19609006 | J. Lipid Res. | 2010 | Zhang Y et al. | The flavoheme reductase Ncb5or protects cells against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced lipotoxicity. |
| 18599738 | J. Lipid Res. | 2008 | Yee JK et al. | Compartmentalization of stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 activity in HepG2 cells. |
| 12777469 | J. Lipid Res. | 2003 | Bulotta A et al. | GLP-1 stimulates glucose-derived de novo fatty acid synthesis and chain elongation during cell differentiation and insulin release. |