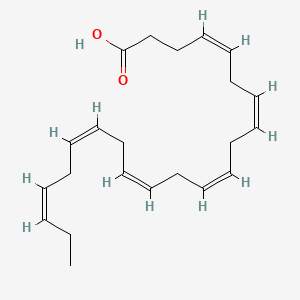
DHA
Dha is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Dha is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Consumption-archaic term for TB, Chronic disease, Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, Oxidation, fatty acid oxidation, Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Metabolism. Dha often locates in Hepatic, Protoplasm, Mucous Membrane, Epithelium and outer membrane. The associated genes with DHA are IMPACT gene, FATE1 gene, GAPDH gene, THOC4 gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are stearidonic acid, Fatty Acids, Total cholesterol, Lipopolysaccharides and Dietary Fatty Acid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Transgenic Model, Animal Disease Models and Arthritis, Experimental.
References related to locations published in J. Lipid Res.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9548590 | J. Lipid Res. | 1998 | Madsen L et al. | Docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acids are differently metabolized in rat liver during mitochondria and peroxisome proliferation. |
| 9684743 | J. Lipid Res. | 1998 | Connor WE et al. | Uneven distribution of desmosterol and docosahexaenoic acid in the heads and tails of monkey sperm. |
| 10681400 | J. Lipid Res. | 2000 | Calviello G et al. | n-3 PUFA dietary supplementation inhibits proliferation and store-operated calcium influx in thymoma cells growing in Balb/c mice. |
| 19023138 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | Tanito M et al. | High levels of retinal membrane docosahexaenoic acid increase susceptibility to stress-induced degeneration. |
| 19018037 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | Bazan NG | Neuroprotectin D1-mediated anti-inflammatory and survival signaling in stroke, retinal degenerations, and Alzheimer's disease. |
| 19571329 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | Gao F et al. | Whole-body synthesis secretion of docosahexaenoic acid from circulating eicosapentaenoic acid in unanesthetized rats. |
| 20382842 | J. Lipid Res. | 2010 | Bazan NG et al. | Rescue and repair during photoreceptor cell renewal mediated by docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1. |
| 20664072 | J. Lipid Res. | 2010 | Morisseau C et al. | Naturally occurring monoepoxides of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid are bioactive antihyperalgesic lipids. |
| 15627650 | J. Lipid Res. | 2005 | Denys A et al. | n-3 PUFAs modulate T-cell activation via protein kinase C-alpha and -epsilon and the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. |
| 18503030 | J. Lipid Res. | 2008 | Farias SE et al. | Formation of eicosanoids, E2/D2 isoprostanes, and docosanoids following decapitation-induced ischemia, measured in high-energy-microwaved rat brain. |
| 22315394 | J. Lipid Res. | 2012 | Rockett BD et al. | Fish oil increases raft size and membrane order of B cells accompanied by differential effects on function. |
| 23801662 | J. Lipid Res. | 2013 | Samieri C et al. | Relationship between diet and plasma long-chain n-3 PUFAs in older people: impact of apolipoprotein E genotype. |
| 23160180 | J. Lipid Res. | 2013 | Al-Hilal M et al. | Genetic variation at the FADS1-FADS2 gene locus influences delta-5 desaturase activity and LC-PUFA proportions after fish oil supplement. |