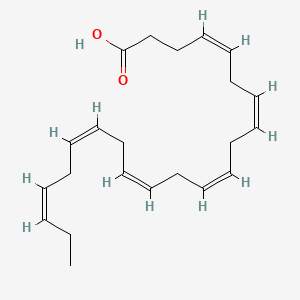
DHA
Dha is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Dha is associated with abnormalities such as Atherosclerosis, Consumption-archaic term for TB, Chronic disease, Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Insulin-Dependent. The involved functions are known as Inflammation, Oxidation, fatty acid oxidation, Fatty Acid Metabolism and Lipid Metabolism. Dha often locates in Hepatic, Protoplasm, Mucous Membrane, Epithelium and outer membrane. The associated genes with DHA are IMPACT gene, FATE1 gene, GAPDH gene, THOC4 gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related lipids are stearidonic acid, Fatty Acids, Total cholesterol, Lipopolysaccharides and Dietary Fatty Acid. The related experimental models are Mouse Model, Transgenic Model, Animal Disease Models and Arthritis, Experimental.
References related to experimental models published in J. Nutr.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23303872 | J. Nutr. | 2013 | Depner CM et al. | Docosahexaenoic acid attenuates hepatic inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis without decreasing hepatosteatosis in a Ldlr(-/-) mouse model of western diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. |
| 23739309 | J. Nutr. | 2013 | Liu Y et al. | Fish oil increases muscle protein mass and modulates Akt/FOXO, TLR4, and NOD signaling in weanling piglets after lipopolysaccharide challenge. |
| 24285691 | J. Nutr. | 2014 | Höper AC et al. | Wax esters from the marine copepod Calanus finmarchicus reduce diet-induced obesity and obesity-related metabolic disorders in mice. |