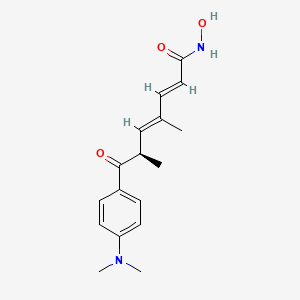
trichostatin A
Trichostatin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Trichostatin is associated with abnormalities such as Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy, PARAGANGLIOMAS 3, abnormal fragmented structure, Disintegration (morphologic abnormality) and Hyperostosis, Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal. The involved functions are known as Acetylation, Cell Differentiation process, histone modification, Gene Silencing and Transcriptional Activation. Trichostatin often locates in CD41a, Hematopoietic System, Chromatin Structure, Blood and Endothelium. The associated genes with Trichostatin are SPI1 gene, CELL Gene, Chromatin, CXCR4 gene and DNMT1 gene. The related lipids are Butyrates, Promega, butyrate, Lipopolysaccharides and Steroids. The related experimental models are Knock-out, Mouse Model, Xenograft Model and Cancer Model.
References related to abnormalities published in J. Virol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11991990 | J. Virol. | 2002 | Gradoville L et al. | Protein kinase C-independent activation of the Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle. |
| 12768031 | J. Virol. | 2003 | Génin P et al. | Impairment of interferon-induced IRF-7 gene expression due to inhibition of ISGF3 formation by trichostatin A. |
| 11264377 | J. Virol. | 2001 | Arthur JL et al. | Herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter activity during latency establishment, maintenance, and reactivation in primary dorsal root neurons in vitro. |