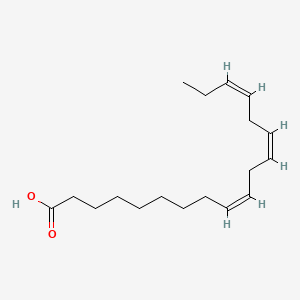
alpha-linolenic acid
Alpha-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Alpha-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, abnormal fragmented structure, Arterial thrombosis and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Signal, Transcription, Genetic, Saturated and Regulation. Alpha-linolenic acid often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Plasma membrane, Hepatic and peroxisome. The associated genes with alpha-linolenic acid are FATE1 gene, volicitin, CYP2U1 gene, CYP1A2 gene and CYP2J2 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Dietary Fatty Acid, stearidonic acid and Fatty Acids, Nonesterified.
References related to functions published in Plant Physiol.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10482670 | Plant Physiol. | 1999 | Koch T et al. | Differential induction of plant volatile biosynthesis in the lima bean by early and late intermediates of the octadecanoid-signaling pathway. |
| 12970495 | Plant Physiol. | 2003 | Schmelz EA et al. | Nitrogen deficiency increases volicitin-induced volatile emission, jasmonic acid accumulation, and ethylene sensitivity in maize. |