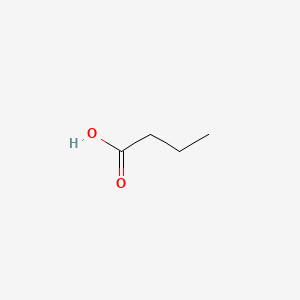
butyric acid
butyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Butyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as PARKINSON DISEASE, LATE-ONSET, Colitis, Autoimmune Diseases, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and PARAGANGLIOMAS 2. The involved functions are known as DNA Methylation, Transcription, Genetic, chromatin modification, Gene Expression and Gene Silencing. Butyric acid often locates in Membrane, Chromatin Structure, Chromosomes, viral nucleocapsid location and Ribosomes. The associated genes with butyric acid are Locus, Genes, Dominant, Genes, rRNA, Genome and Chromatin. The related lipids are Butyrates, butyrate, Promega, Butyric Acids and Butyric Acid.
References related to abnormalities published in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9294201 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | 1997 | Ohno Y et al. | Macrophage inflammatory protein-2: chromosomal regulation in rat small intestinal epithelial cells. |
| 9159154 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | 1997 | Chen WY et al. | Reactivation of silenced, virally transduced genes by inhibitors of histone deacetylase. |
| 16785443 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | 2006 | Poon AP et al. | ICP0 and the US3 protein kinase of herpes simplex virus 1 independently block histone deacetylation to enable gene expression. |