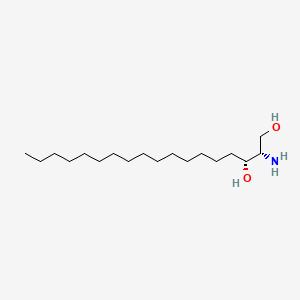
Sphinganine
Sphinganine is a lipid of Sphingolipids (SP) class. Sphinganine is associated with abnormalities such as Sphingolipidoses, CLEFT LIP, CONGENITAL HEALED, Aortic aneurysm, familial thoracic 4, Morphologically altered structure and Atherosclerosis. The involved functions are known as Transcription, Genetic, Signal, Muscle Contraction, biological adaptation to stress and Gene Expression. Sphinganine often locates in Tissue membrane, Membrane, Protoplasm, Plasma membrane and Cytoplasmic. The associated genes with Sphinganine are SLC33A1 gene, HM13 gene, P4HTM gene, SPHK1 gene and SPHK2 gene. The related lipids are Sphingolipids, Phosphatidylserines, Sterols, Fatty Acids and inositolphosphorylceramide. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Knock-out.
References related to functions published in Toxicol. Sci.
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11248151 | Toxicol. Sci. | 2001 | Mathur S et al. | Fumonisin B(1) increases serum sphinganine concentration but does not alter serum sphingosine concentration or induce cardiovascular changes in milk-fed calves. |
| 11248152 | Toxicol. Sci. | 2001 | Mathur S et al. | Fumonisin B(1) is hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic in milk-fed calves. |
| 10869473 | Toxicol. Sci. | 2000 | Smith GW et al. | Purified fumonisin B(1) decreases cardiovascular function but does not alter pulmonary capillary permeability in swine. |
| 15829618 | Toxicol. Sci. | 2005 | Hsiao SH et al. | Effects of exogenous sphinganine, sphingosine, and sphingosine-1-phosphate on relaxation and contraction of porcine thoracic aortic and pulmonary arterial rings. |
| 16221962 | Toxicol. Sci. | 2006 | Voss KA et al. | Toxic effects of fumonisin in mouse liver are independent of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. |