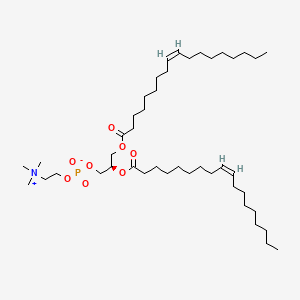
1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine
1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine is a lipid of Glycerophospholipids (GP) class. 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine is associated with abnormalities such as Exanthema, Renal tubular disorder, Nodule, Gigantism and Mycoses. The involved functions are known as Lysis, Encapsulation, Process, Uptake and Flow or discharge. 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine often locates in Cytoplasmic matrix, Endosomes, soluble, Endoplasmic Reticulum and Membrane. The associated genes with 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-Glycero-3-Phosphocholine are P4HTM gene, synthetic peptide, BCAR1 gene, PCNA gene and CNTNAP1 gene. The related lipids are Liposomes, 1,2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine, 1,2-distearoylphosphatidylethanolamine, Butanols and Cardiolipins. The related experimental models are Mouse Model and Xenograft Model.
References related to abnormalities published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21421858 | Clin. Cancer Res. | 2011 | Chakravarty D et al. | Therapeutic targeting of PELP1 prevents ovarian cancer growth and metastasis. |
| 19850632 | Clin. Chem. | 2009 | Chalbot S et al. | Cerebrospinal fluid secretory Ca2+-dependent phospholipase A2 activity is increased in Alzheimer disease. |
| 20430760 | Cancer Res. | 2010 | Tanaka T et al. | Sustained small interfering RNA delivery by mesoporous silicon particles. |
| 16914580 | Clin. Cancer Res. | 2006 | Halder J et al. | Focal adhesion kinase targeting using in vivo short interfering RNA delivery in neutral liposomes for ovarian carcinoma therapy. |
| 21957230 | J. Natl. Cancer Inst. | 2011 | Nick AM et al. | Silencing of p130cas in ovarian carcinoma: a novel mechanism for tumor cell death. |
| 27480806 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | 2016 | Freudenthal O et al. | Nanoscale investigation of the interaction of colistin with model phospholipid membranes by Langmuir technique, and combined infrared and force spectroscopies. |
| 27349734 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | 2016 | Kettiger H et al. | Interactions between silica nanoparticles and phospholipid membranes. |
| 25223717 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | 2015 | Chulkov EG et al. | Membrane dipole modifiers modulate single-length nystatin channels via reducing elastic stress in the vicinity of the lipid mouth of a pore. |