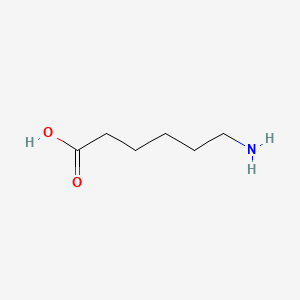
6-aminohexanoic acid
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid.
References related to functions published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9746604 | Infect. Immun. | 1998 | Kukkonen M et al. | Identification of two laminin-binding fimbriae, the type 1 fimbria of Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium and the G fimbria of Escherichia coli, as plasminogen receptors. |
| 9746606 | Infect. Immun. | 1998 | Pantzar M et al. | Plasminogen binding and activation at the surface of Helicobacter pylori CCUG 17874. |
| 9884383 | Circulation | 1999 Jan 5-12 | Munoz JJ et al. | Is epsilon-aminocaproic acid as effective as aprotinin in reducing bleeding with cardiac surgery?: a meta-analysis. |
| 11568067 | Circulation | 2001 | Greilich PE et al. | Aprotinin but not epsilon-aminocaproic acid decreases interleukin-10 after cardiac surgery with extracorporeal circulation: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients receiving aprotinin and epsilon-aminocaproic acid. |
| 11734579 | J. Lipid Res. | 2001 | Gaubatz JW et al. | Isolation, quantitation, and characterization of a stable complex formed by Lp[a] binding to triglyceride-rich lipoproteins. |
| 12620858 | Appl. Environ. Microbiol. | 2003 | Mikolasch A et al. | Synthesis of imidazol-2-yl amino acids by using cells from alkane-oxidizing bacteria. |
| 19050037 | CMAJ | 2009 | Henry D et al. | The safety of aprotinin and lysine-derived antifibrinolytic drugs in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. |
| 19494241 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | 2009 | Aplin AC et al. | Vascular regression and survival are differentially regulated by MT1-MMP and TIMPs in the aortic ring model of angiogenesis. |
| 17283031 | Drug Metab. Dispos. | 2007 | Tirand L et al. | Metabolic profile of a peptide-conjugated chlorin-type photosensitizer targeting neuropilin-1: an in vivo and in vitro study. |
| 18658042 | Stroke | 2008 | Starke RM et al. | Impact of a protocol for acute antifibrinolytic therapy on aneurysm rebleeding after subarachnoid hemorrhage. |
| 21893178 | Int J Pharm | 2012 | Shi J et al. | Reducible HPMA-co-oligolysine copolymers for nucleic acid delivery. |
| 21110983 | J. Mol. Biol. | 2011 | Badyal SK et al. | Mechanism of the Ca²+-dependent interaction between S100A4 and tail fragments of nonmuscle myosin heavy chain IIA. |
| 20228346 | J. Exp. Biol. | 2010 | Barrozo RB et al. | Mating-induced transient inhibition of responses to sex pheromone in a male moth is not mediated by octopamine or serotonin. |
| 19542079 | J. Med. Genet. | 2010 | Gerards M et al. | Defective complex I assembly due to C20orf7 mutations as a new cause of Leigh syndrome. |
| 19152998 | Ultrasound Med Biol | 2009 | Miller DL et al. | Glomerular capillary hemorrhage induced in rats by diagnostic ultrasound with gas-body contrast agent produces intratubular obstruction. |
| 18656632 | Surgery | 2008 | Roztocil E et al. | Insulin-induced epidermal growth factor activation in vascular smooth muscle cells is ADAM-dependent. |
| 18545222 | Mol. Ther. | 2008 | Jearawiriyapaisarn N et al. | Sustained dystrophin expression induced by peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomers in the muscles of mdx mice. |
| 17574041 | J. Surg. Res. | 2007 | Roztocil E et al. | Mechanisms of kringle fragment of urokinase-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. |
| 17533182 | Circulation | 2007 | Brown JR et al. | Meta-analysis comparing the effectiveness and adverse outcomes of antifibrinolytic agents in cardiac surgery. |
| 17138746 | J. Nucl. Med. | 2006 | Wild D et al. | [Lys40(Ahx-DTPA-111In)NH2]exendin-4, a very promising ligand for glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor targeting. |
| 16920561 | Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. | 2006 | Wanko SO et al. | Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage: retrospective review of clinical outcome in allogeneic transplant recipients treated with aminocaproic acid. |
| 16849568 | Cancer Res. | 2006 | Wang H et al. | Differential binding of plasminogen, plasmin, and angiostatin4.5 to cell surface beta-actin: implications for cancer-mediated angiogenesis. |
| 15477642 | Oncologist | 2004 | Pereira J and Phan T | Management of bleeding in patients with advanced cancer. |
| 14718842 | J. Vasc. Surg. | 2004 | Tanski WJ et al. | Domain-dependent action of urokinase on smooth muscle cell responses. |
| 12407382 | J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. | 2002 | Quin JA et al. | Predictors of pericardial effusion after orthotopic heart transplantation. |
| 13939069 | J. Clin. Pathol. | 1963 | NOUR-ELDIN F and DRAISEY TF | Hepatic and cardiac necrosis in a patient with prostatic carcinoma given 6-aminocaproic acid. |