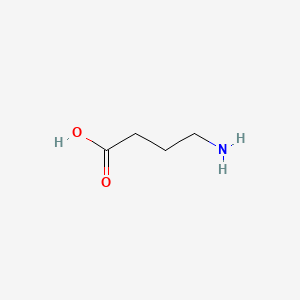
4-aminobutyric acid
4-aminobutyric acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 4-aminobutyric acid is associated with abnormalities such as Epilepsy and Premenstrual syndrome. The involved functions are known as Binding (Molecular Function), neuron survival, Process, Uptake and physiological aspects. 4-aminobutyric acid often locates in Microglial, Neurofilament, Neuraxis, Brain region and Neurites. The associated genes with 4-aminobutyric acid are arginine methyl ester, SLC33A1 gene, NKS1 gene, P4HTM gene and ITSN2 gene. The related lipids are pregnenolone sulfate, pregnane-20-one, Pregnanes, Steroids and endogenous steroids.
References related to functions published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9262347 | J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. | 1997 | Sousa A and Ticku MK | Interactions of the neurosteroid dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate with the GABA(A) receptor complex reveals that it may act via the picrotoxin site. |
| 10400943 | J. Neurophysiol. | 1999 | Haage D and Johansson S | Neurosteroid modulation of synaptic and GABA-evoked currents in neurons from the rat medial preoptic nucleus. |
| 9603942 | J. Biol. Chem. | 1998 | Ciesielski-Treska J et al. | Chromogranin A induces a neurotoxic phenotype in brain microglial cells. |
| 11495904 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2001 | Adkins CE et al. | alpha4beta3delta GABA(A) receptors characterized by fluorescence resonance energy transfer-derived measurements of membrane potential. |