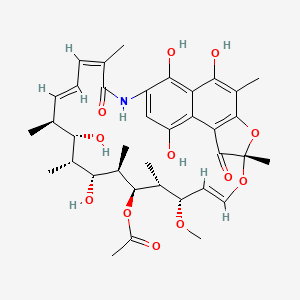
Rifamycin SV
Rifamycin SV is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Rifamycin sv is associated with abnormalities such as Cholestasis, Infection, Dysentery, Soft Tissue Infections and Osteomyelitis. The involved functions are known as Uptake, Excretory function, Drug Kinetics, inhibitors and anaphylaxis. Rifamycin sv often locates in Hepatic, Blood, soluble, Entire gastrointestinal tract and Membrane. The associated genes with Rifamycin SV are SLCO1C1 gene, SLCO1B1 gene, ABCB11 gene and SLC10A1 gene.
References related to functions published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10381771 | J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. | 1999 | van Montfoort JE et al. | Hepatic uptake of the magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent gadoxetate by the organic anion transporting polypeptide Oatp1. |
| 14986259 | Clin. Infect. Dis. | 2004 | Nettles RE et al. | Risk factors for relapse and acquired rifamycin resistance after directly observed tuberculosis treatment: a comparison by HIV serostatus and rifamycin use. |