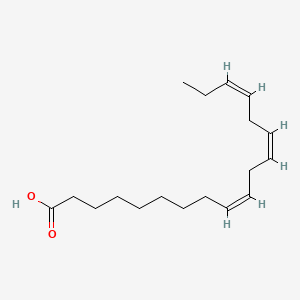
alpha-linolenic acid
Alpha-linolenic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Alpha-linolenic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Coronary heart disease, abnormal fragmented structure, Arterial thrombosis and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. The involved functions are known as Anabolism, Signal, Transcription, Genetic, Saturated and Regulation. Alpha-linolenic acid often locates in Blood, Body tissue, Plasma membrane, Hepatic and peroxisome. The associated genes with alpha-linolenic acid are FATE1 gene, volicitin, CYP2U1 gene, CYP1A2 gene and CYP2J2 gene. The related lipids are Fatty Acids, Dietary Fatty Acid, stearidonic acid and Fatty Acids, Nonesterified.
References related to functions published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14729912 | Plant Cell | 2004 | Truitt CL et al. | A plasma membrane protein from Zea mays binds with the herbivore elicitor volicitin. |
| 18802197 | J. Lipid Res. | 2009 | McNamara RK et al. | Perinatal n-3 fatty acid deficiency selectively reduces myo-inositol levels in the adult rat PFC: an in vivo (1)H-MRS study. |
| 27133376 | Neuropharmacology | 2016 | Bourourou M et al. | Alpha-linolenic acid given as enteral or parenteral nutritional intervention against sensorimotor and cognitive deficits in a mouse model of ischemic stroke. |
| 26869088 | Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids | 2016 | Taha AY et al. | Threshold changes in rat brain docosahexaenoic acid incorporation and concentration following graded reductions in dietary alpha-linolenic acid. |