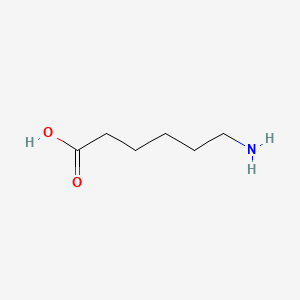
6-aminohexanoic acid
6-aminohexanoic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. 6-aminohexanoic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Blood Clot, Myocardial Infarction, Cerebrovascular accident, Renal impairment and Scoliosis, unspecified. The involved functions are known as Fibrinolysis, Agent, Hemorrhage, plasminogen activation and inhibitors. 6-aminohexanoic acid often locates in Chest, Blood, Body tissue, peritoneal and Plasma membrane. The associated genes with 6-aminohexanoic acid are P4HTM gene, BSND gene, MTPN gene, NDUFS4 gene and Homologous Gene. The related lipids are Phosphatidylserines and Butyric Acid.
References related to genes published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12620858 | Appl. Environ. Microbiol. | 2003 | Mikolasch A et al. | Synthesis of imidazol-2-yl amino acids by using cells from alkane-oxidizing bacteria. |
| 19050037 | CMAJ | 2009 | Henry D et al. | The safety of aprotinin and lysine-derived antifibrinolytic drugs in cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis. |
| 19494241 | Am. J. Physiol., Cell Physiol. | 2009 | Aplin AC et al. | Vascular regression and survival are differentially regulated by MT1-MMP and TIMPs in the aortic ring model of angiogenesis. |
| 21857014 | Br J Anaesth | 2011 | Martin K et al. | Switch from aprotinin to ε-aminocaproic acid: impact on blood loss, transfusion, and clinical outcome in neonates undergoing cardiac surgery. |
| 18658042 | Stroke | 2008 | Starke RM et al. | Impact of a protocol for acute antifibrinolytic therapy on aneurysm rebleeding after subarachnoid hemorrhage. |
| 17574041 | J. Surg. Res. | 2007 | Roztocil E et al. | Mechanisms of kringle fragment of urokinase-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. |
| 14718842 | J. Vasc. Surg. | 2004 | Tanski WJ et al. | Domain-dependent action of urokinase on smooth muscle cell responses. |