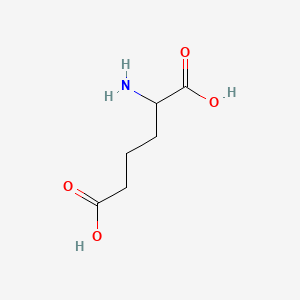
Aminoadipic acid
Aminoadipic acid is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Aminoadipic acid is associated with abnormalities such as Diabetes and Proliferative retinopathy NOS. The involved functions are known as Uptake, Process, lysine catabolism, Pressure- physical agent and Proteolysis. Aminoadipic acid often locates in Protoplasm, Chromosomes, Astrocytic, Basal lamina and Cytoplasmic matrix. The associated genes with Aminoadipic acid are Homologous Gene, Excitatory Amino Acids, allysine, Diaminopimelic Acid and Gene Clusters.
References related to genes published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10613839 | Genome Res. | 1999 | Nishida H et al. | A prokaryotic gene cluster involved in synthesis of lysine through the amino adipate pathway: a key to the evolution of amino acid biosynthesis. |
| 20720223 | Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. | 2011 | Shen W et al. | Submacular DL-alpha-aminoadipic acid eradicates primate photoreceptors but does not affect luteal pigment or the retinal vasculature. |
| 19854833 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2009 | Fan X et al. | Mechanism of lysine oxidation in human lens crystallins during aging and in diabetes. |
| 14766586 | Appl. Environ. Microbiol. | 2004 | Naranjo L et al. | Inactivation of the lys7 gene, encoding saccharopine reductase in Penicillium chrysogenum, leads to accumulation of the secondary metabolite precursors piperideine-6-carboxylic acid and pipecolic acid from alpha-aminoadipic acid. |
| 19460904 | Diabetes Care | 2009 | Bloomgarden ZT | Cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy. |