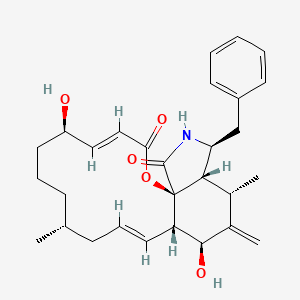
CYTOCHALASIN B
CYTOCHALASIN B is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Cytochalasin b is associated with abnormalities such as Renal tubular disorder and Chagas Disease. The involved functions are known as Membrane Protein Traffic, inhibitors, Metabolic Inhibition, Biochemical Pathway and Increased Sensitivy. Cytochalasin b often locates in Cytoplasmic matrix, Plasma membrane, Microtubules, Extracellular and Protoplasm. The associated genes with CYTOCHALASIN B are SLC2A2 gene, PFDN5 gene, SLC2A1 gene, OMG gene and SPEN gene. The related lipids are Steroids, Lipopolysaccharides and Liposomes. The related experimental models are Xenograft Model.
References related to genes published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11739114 | Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. | 2002 | Miyata Y et al. | P-gp-induced modulation of regulatory volume increase occurs via PKC in mouse proximal tubule. |
| 10754332 | J. Immunol. | 2000 | Mócsai A et al. | Kinase pathways in chemoattractant-induced degranulation of neutrophils: the role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activated by Src family kinases. |
| 15033941 | Glycobiology | 2004 | Durán JM et al. | D-mannose transport and metabolism in isolated enterocytes. |
| 23038726 | J. Exp. Biol. | 2013 | Driedzic WR et al. | Glucose uptake and metabolism by red blood cells from fish with different extracellular glucose levels. |
| 24127585 | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. | 2013 | Iancu CV et al. | Crystal structure of a glucose/H+ symporter and its mechanism of action. |
| 10825458 | Biochim. Biophys. Acta | 2000 | Lachaal M et al. | Characterization and partial purification of liver glucose transporter GLUT2. |
| 24799603 | J. Leukoc. Biol. | 2014 | Dib K et al. | The histamine H4 receptor is a potent inhibitor of adhesion-dependent degranulation in human neutrophils. |