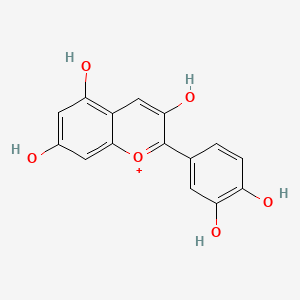
Cyanidin
Cyanidin is a lipid of Polyketides (PK) class. Cyanidin is associated with abnormalities such as Consumption-archaic term for TB, furuncle, Obesity, Cardiovascular Diseases and Endothelial dysfunction. The involved functions are known as anthocyanin biosynthetic process, Regulation, flavonoid biosynthetic process, Anabolism and anthocyanin metabolic process. Cyanidin often locates in Body tissue, integral to membrane, Autonomic nervous system, Blood and Tissue membrane. The associated genes with Cyanidin are anthocyanidin synthase, SLC2A8 gene, EPB41L2 gene, NKS1 gene and GLUCOSIDASE. The related lipids are Butanols. The related experimental models are Knock-out.
References related to locations published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17709440 | J. Nutr. | 2007 | Vitaglione P et al. | Protocatechuic acid is the major human metabolite of cyanidin-glucosides. |
| 20085894 | Mol Plant | 2010 | Pourcel L et al. | The formation of Anthocyanic Vacuolar Inclusions in Arabidopsis thaliana and implications for the sequestration of anthocyanin pigments. |
| 15226277 | Hypertension | 2004 | Xu JW et al. | Upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase by cyanidin-3-glucoside, a typical anthocyanin pigment. |
| 11316805 | J. Biol. Chem. | 2001 | Nakajima J et al. | Reaction mechanism from leucoanthocyanidin to anthocyanidin 3-glucoside, a key reaction for coloring in anthocyanin biosynthesis. |