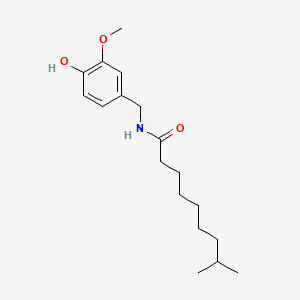
Capsaicin
Capsaicin is a lipid of Fatty Acyls (FA) class. Capsaicin is associated with abnormalities such as Morphologically altered structure. The involved functions are known as inhibitors, Regulation, metaplastic cell transformation, Biochemical Pathway and Uptake. Capsaicin often locates in Tissue fiber, Mucous Membrane, Nerve Endings, group Ia axon and Membrane. The associated genes with Capsaicin are TRPV1 gene, WT-1, MAP1LC3A gene, EIF2S3 gene and SLC33A1 gene. The related experimental models are Transgenic Model.
References related to locations published in Others
| PMID | Journal | Published Date | Author | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19139269 | J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. | 2009 | Oh SH and Lim SC | Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy/apoptosis induced by capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-nonenamide) and dihydrocapsaicin is regulated by the extent of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in WI38 lung epithelial fibroblast cells. |